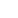
Printed circuit board Assembly
What is the PCBA?
In a nutshell
PCBA(Printed circuits board) manufacturing refers to the entire production process of installing electronic components (such as chips, resistors, capacitors, etc.) onto an empty printed circuit board (PCB), forming electrical connections, and ultimately transforming it into a functional circuit board assembly (PCBA).
You can understand it as: PCB (bare board) + component assembly = PCBA (finished board).
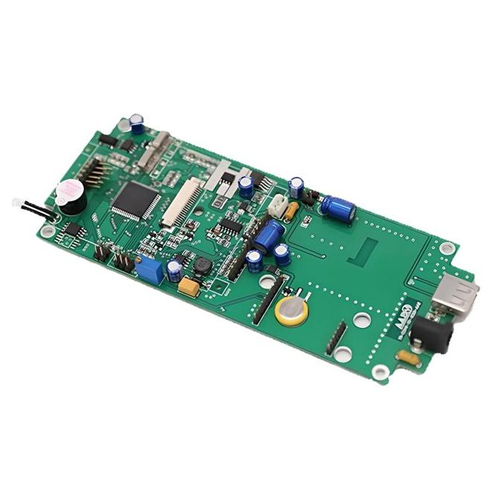

Detailed breakdown
To better understand, we can break down PCBA manufacturing into several key steps:
1. Preparatory work: PCB manufacturing and component procurement
PCB manufacturing: First, an empty circuit board (PCB) needs to be fabricated based on the circuit design. It provides the base for component installation and the electrical connection lines.
Component procurement and inspection: Purchase all required electronic components based on the design documents (BOM list) and inspect them to ensure they are of qualified quality.
2. Core assembly processes: SMT and THT
This is the core link in PCBA manufacturing, mainly including two technologies:
A. SMT (Surface Mount Technology)
This is currently the mainstream assembly method, suitable for small and lightweight components.
Solder paste printing: Through a steel mesh, solder paste is precisely printed onto the pads of a PCB.
Component placement: Use a high-speed surface mount technology (SMT) placement machine to precisely place SMT components onto solder pads coated with solder paste.
Reflow soldering: The PCB with components attached is passed through a reflow soldering oven. The high temperature inside the oven melts the solder paste, which solidifies after cooling, thus firmly soldering the components onto the PCB.
This is a simplified schematic diagram of an SMT production line: solder paste printing → surface mount technology (SMT) → reflow soldering
B. THT (Through-Hole Mounting Technology)
It is suitable for larger components that need to withstand significant mechanical stress or power.
Component insertion: Automatically or manually insert the pins of components into the corresponding through-holes on the PCB.
Wave soldering: Pass molten solder waves through the bottom of the PCB, allowing the solder to wet and fill the through holes, and then solder the pins of the components onto the board.
On many complex boards, SMT and THT processes are used in combination.
3. Post-processing and testing
After assembly is completed, it is far from over. Quality control is of vital importance.
Cleaning: Remove residual flux and other contaminants after welding.
Detection and Testing
AOI (Automatic Optical Inspection) : It uses cameras to automatically detect welding defects such as short circuits, false welds, and offsets.
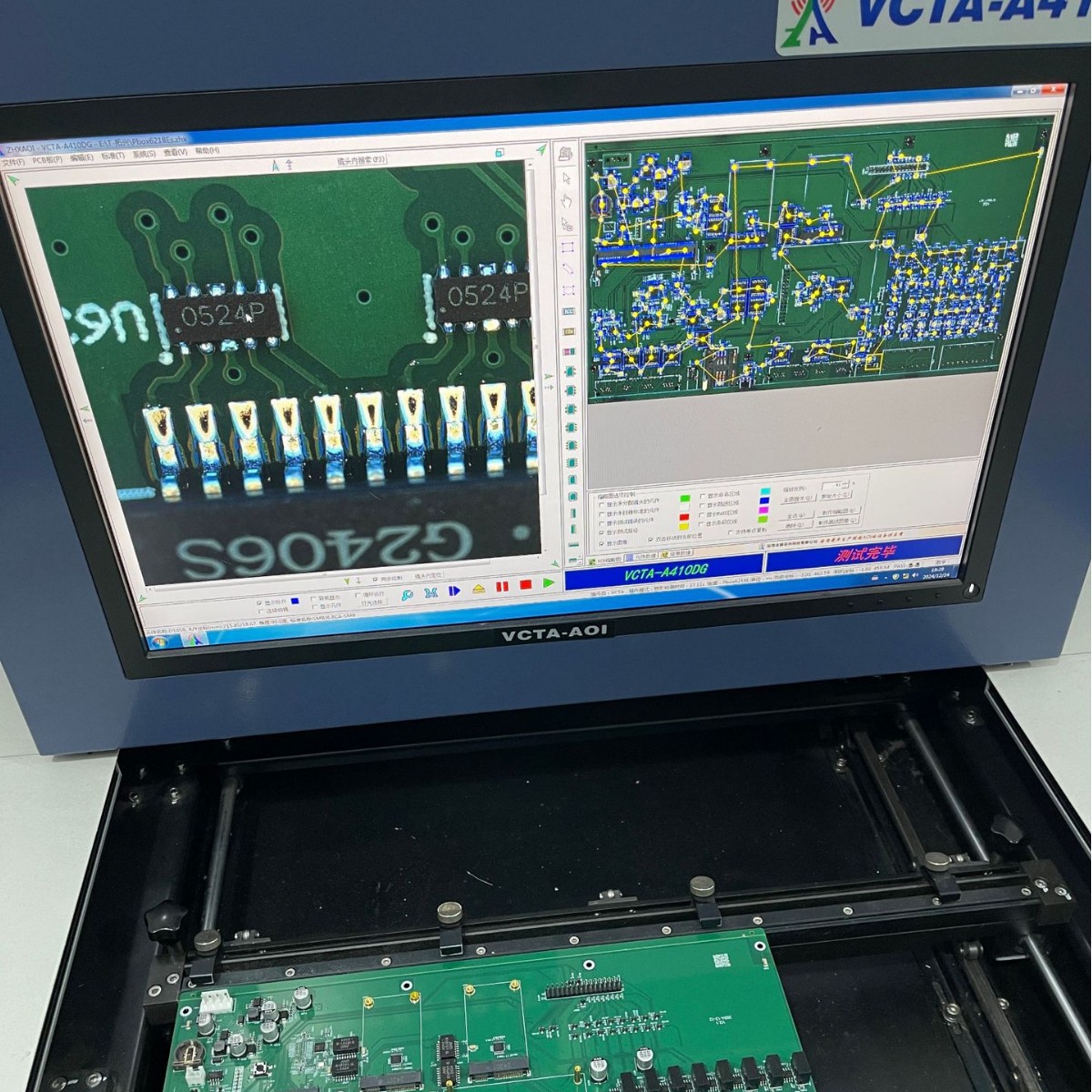


X-Ray inspection: It is used to check the quality of solder joints hidden beneath components (such as BGA packages).
ICT (Online Testing) : By using test probes to touch the test points on the PCB, it checks whether the components are installed correctly and whether there are open circuits or short circuits.
FCT (Functional Testing) : It simulates the real working environment of the final PCBA product to test whether its overall functions are normal. This is the most crucial testing stage.
Conformal coating: For PCBA that may operate in harsh environments (such as high humidity, dust, and corrosive gases), a special protective coating is sprayed to enhance its reliability and lifespan.
Program burning: If necessary, firmware or software programs will be burned onto the main control chip on the board.


We provide a full range of one-stop electronic components supply chain and manufacturing solutions for customers from all over the world.
Tell: +86-134 8018 3028(Same as Wechat)
Web: www.icslove.com
Skype: jorvih
Add: NO402,4F Xinhongtian building, Fuhai Industrial Zone ,Bao'an district, Shenzhen China.

